CMC-Bench: Towards a New Paradigm of Visual Signal Compression
Chunyi Li, Xiele Wu, Haoning Wu, Donghui Feng, Zicheng Zhang, Guo Lu, Xiongkuo Min, Xiaohong Liu, Guangtao Zhai, Weisi Lin
2024-06-14
Summary
This paper presents CMC-Bench, a new benchmark designed to evaluate how well different models can compress images into very small sizes while maintaining quality. It focuses on a method called Cross Modality Compression (CMC) that uses both text and images together to achieve better compression.
What's the problem?
Ultra-low bitrate image compression is difficult because it requires reducing the size of image files significantly without losing important details or quality. Traditional methods often struggle with this, especially when it comes to keeping the original look of the image intact. Additionally, existing compression techniques may not effectively use the relationship between images and text to improve results.
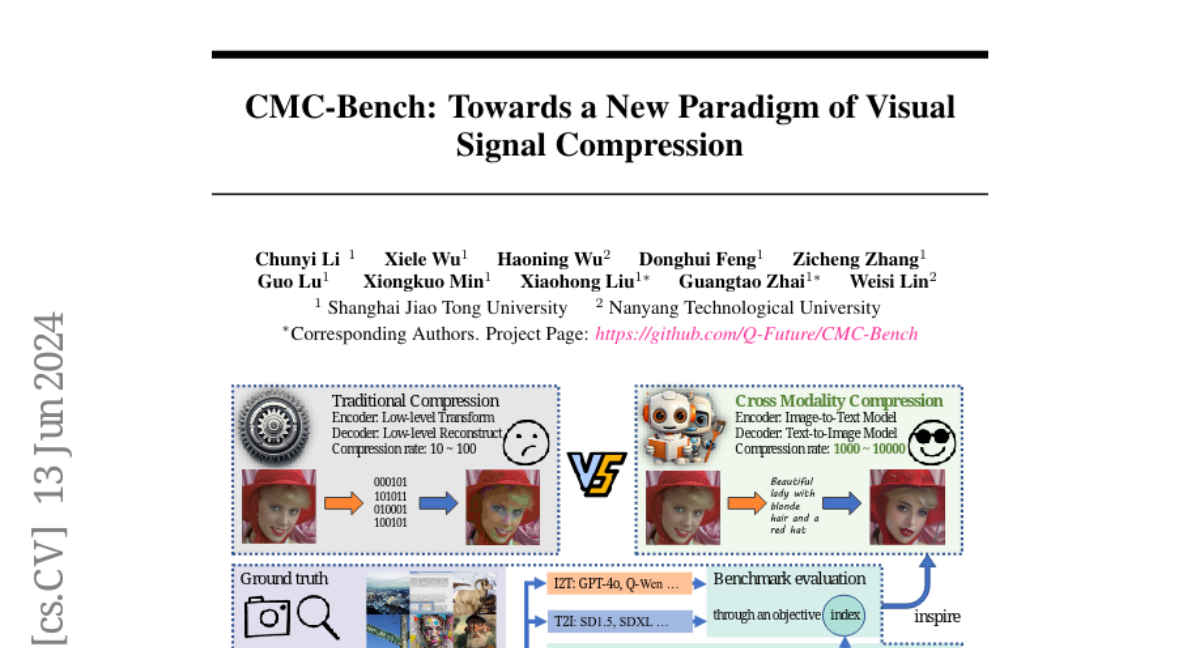
What's the solution?
To tackle these challenges, the authors created CMC-Bench, which tests how well Image-to-Text (I2T) and Text-to-Image (T2I) models perform in compressing images. The benchmark includes a large dataset of 18,000 and 40,000 images, respectively, along with subjective ratings from human experts to assess how well each model compresses images while preserving their quality. The study shows that certain combinations of I2T and T2I models can outperform traditional image compression methods at very low bitrates.
Why it matters?
This research is significant because it opens up new possibilities for more efficient image compression techniques that could be used in various applications, such as streaming videos or storing images on devices with limited space. By encouraging collaboration among developers of large multimodal models, CMC-Bench aims to advance the technology of visual signal compression and improve how we handle images in digital formats.
Abstract
Ultra-low bitrate image compression is a challenging and demanding topic. With the development of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), a Cross Modality Compression (CMC) paradigm of Image-Text-Image has emerged. Compared with traditional codecs, this semantic-level compression can reduce image data size to 0.1\% or even lower, which has strong potential applications. However, CMC has certain defects in consistency with the original image and perceptual quality. To address this problem, we introduce CMC-Bench, a benchmark of the cooperative performance of Image-to-Text (I2T) and Text-to-Image (T2I) models for image compression. This benchmark covers 18,000 and 40,000 images respectively to verify 6 mainstream I2T and 12 T2I models, including 160,000 subjective preference scores annotated by human experts. At ultra-low bitrates, this paper proves that the combination of some I2T and T2I models has surpassed the most advanced visual signal codecs; meanwhile, it highlights where LMMs can be further optimized toward the compression task. We encourage LMM developers to participate in this test to promote the evolution of visual signal codec protocols.