GKG-LLM: A Unified Framework for Generalized Knowledge Graph Construction
Jian Zhang, Bifan Wei, Shihao Qi, haiping Zhu, Jun Liu, Qika Lin
2025-03-20
Summary
This paper is about creating a single AI system that can build different types of knowledge graphs, which are like organized databases of information.
What's the problem?
Currently, different knowledge graphs are built separately, which wastes resources and misses connections between them.
What's the solution?
The researchers created a system called GKG-LLM that can learn to build different types of knowledge graphs at the same time, by feeding it data from different sources and training it in stages.
Why it matters?
This work matters because it can lead to more efficient and comprehensive AI systems that can understand and use knowledge from various sources.
Abstract
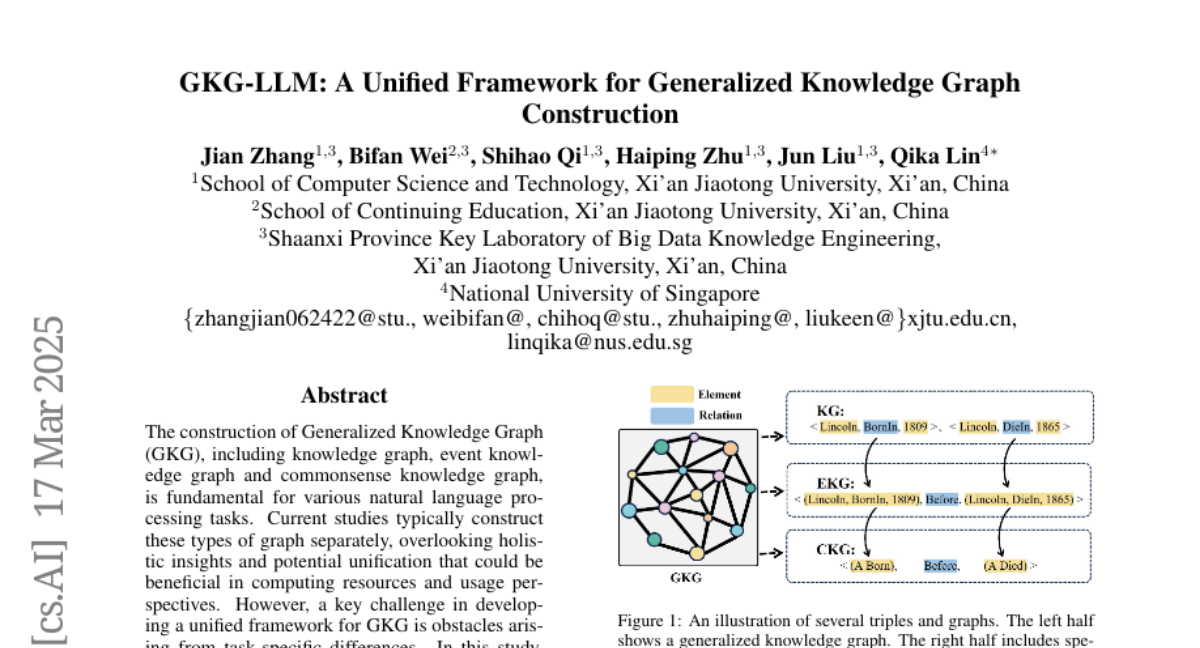
The construction of Generalized Knowledge Graph (GKG), including knowledge graph, event knowledge graph and commonsense knowledge graph, is fundamental for various natural language processing tasks. Current studies typically construct these types of graph separately, overlooking holistic insights and potential unification that could be beneficial in computing resources and usage perspectives. However, a key challenge in developing a unified framework for GKG is obstacles arising from task-specific differences. In this study, we propose a unified framework for constructing generalized knowledge graphs to address this challenge. First, we collect data from 15 sub-tasks in 29 datasets across the three types of graphs, categorizing them into in-sample, counter-task, and out-of-distribution (OOD) data. Then, we propose a three-stage curriculum learning fine-tuning framework, by iteratively injecting knowledge from the three types of graphs into the Large Language Models. Extensive experiments show that our proposed model improves the construction of all three graph types across in-domain, OOD and counter-task data.