HoloPart: Generative 3D Part Amodal Segmentation
Yunhan Yang, Yuan-Chen Guo, Yukun Huang, Zi-Xin Zou, Zhipeng Yu, Yangguang Li, Yan-Pei Cao, Xihui Liu
2025-04-11
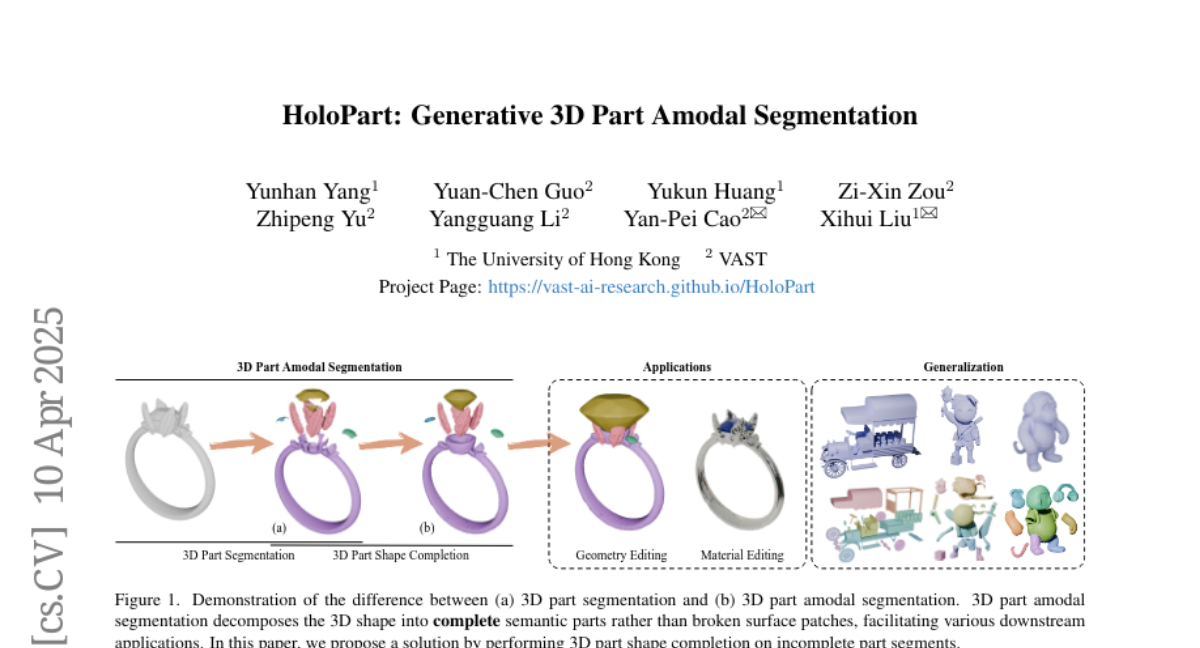
Summary
This paper talks about HoloPart, a new method for breaking down 3D objects into their full parts, even if some parts are hidden or blocked from view. The goal is to help computers understand and work with 3D shapes more completely, which is important for things like animation and 3D design.
What's the problem?
The main problem is that most current tools for 3D part segmentation can only identify the parts of an object that you can actually see. They can't figure out the entire shape of parts that are hidden behind or inside other parts, which limits how useful these tools are for creating or editing 3D models.
What's the solution?
To solve this, the researchers created a two-step process. First, they use existing methods to find the visible parts of a 3D object. Then, they use their new model, HoloPart, which is designed to fill in the missing pieces and guess the full shape of each part, even if it's hidden. HoloPart uses a special kind of AI called a diffusion model, which pays attention to both the small details and the overall shape, so the completed parts look realistic and fit together well.
Why it matters?
This work matters because it allows for much more accurate and complete understanding of 3D objects, which can make 3D design, animation, and editing easier and more powerful. By being able to work with the whole shape, not just what you can see, artists and engineers can create better models and animations, and computers can help with more creative and technical tasks in 3D.
Abstract
3D part amodal segmentation--decomposing a 3D shape into complete, semantically meaningful parts, even when occluded--is a challenging but crucial task for 3D content creation and understanding. Existing 3D part segmentation methods only identify visible surface patches, limiting their utility. Inspired by 2D amodal segmentation, we introduce this novel task to the 3D domain and propose a practical, two-stage approach, addressing the key challenges of inferring occluded 3D geometry, maintaining global shape consistency, and handling diverse shapes with limited training data. First, we leverage existing 3D part segmentation to obtain initial, incomplete part segments. Second, we introduce HoloPart, a novel diffusion-based model, to complete these segments into full 3D parts. HoloPart utilizes a specialized architecture with local attention to capture fine-grained part geometry and global shape context attention to ensure overall shape consistency. We introduce new benchmarks based on the ABO and PartObjaverse-Tiny datasets and demonstrate that HoloPart significantly outperforms state-of-the-art shape completion methods. By incorporating HoloPart with existing segmentation techniques, we achieve promising results on 3D part amodal segmentation, opening new avenues for applications in geometry editing, animation, and material assignment.