LLaMA-Mesh: Unifying 3D Mesh Generation with Language Models
Zhengyi Wang, Jonathan Lorraine, Yikai Wang, Hang Su, Jun Zhu, Sanja Fidler, Xiaohui Zeng
2024-11-15
Summary
This paper introduces MVideo, a new framework for generating videos from text descriptions that allows for more complex and precise actions through advanced motion control techniques.
What's the problem?
Current text-to-video (T2V) models often have difficulty creating videos that feature clear and intricate actions. This is mainly because the text prompts used to describe these actions are not detailed enough to convey the necessary motion information.
What's the solution?
To solve this problem, the authors developed MVideo, which uses mask sequences as an additional input to better represent the intended actions. By combining this with advanced vision models like GroundingDINO and SAM2, MVideo can automatically generate these mask sequences, making the video generation process more efficient and effective. The framework allows users to modify either the text prompts or the motion conditions independently, or both together, enabling the creation of videos with more dynamic and complex actions.
Why it matters?
This research is significant because it improves how machines can generate videos that accurately reflect detailed actions described in text. By enhancing the capabilities of T2V models, MVideo sets a new standard for video generation technology, which can be applied in various fields such as entertainment, education, and virtual reality.
Abstract
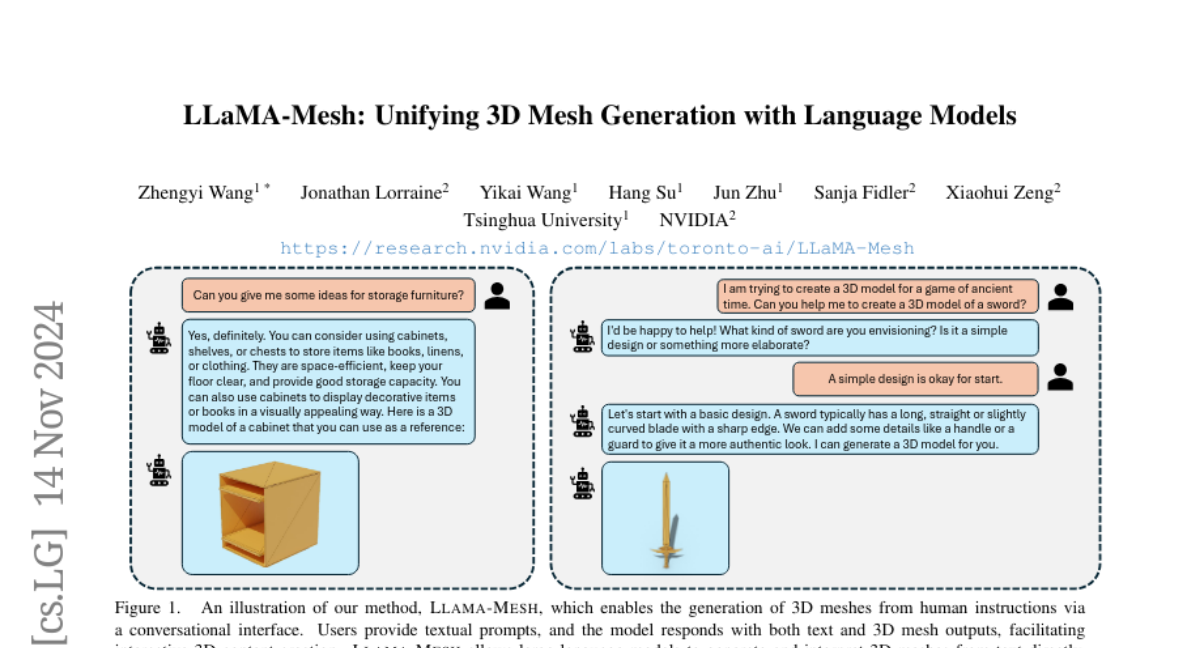
This work explores expanding the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) pretrained on text to generate 3D meshes within a unified model. This offers key advantages of (1) leveraging spatial knowledge already embedded in LLMs, derived from textual sources like 3D tutorials, and (2) enabling conversational 3D generation and mesh understanding. A primary challenge is effectively tokenizing 3D mesh data into discrete tokens that LLMs can process seamlessly. To address this, we introduce LLaMA-Mesh, a novel approach that represents the vertex coordinates and face definitions of 3D meshes as plain text, allowing direct integration with LLMs without expanding the vocabulary. We construct a supervised fine-tuning (SFT) dataset enabling pretrained LLMs to (1) generate 3D meshes from text prompts, (2) produce interleaved text and 3D mesh outputs as required, and (3) understand and interpret 3D meshes. Our work is the first to demonstrate that LLMs can be fine-tuned to acquire complex spatial knowledge for 3D mesh generation in a text-based format, effectively unifying the 3D and text modalities. LLaMA-Mesh achieves mesh generation quality on par with models trained from scratch while maintaining strong text generation performance.