M-RewardBench: Evaluating Reward Models in Multilingual Settings
Srishti Gureja, Lester James V. Miranda, Shayekh Bin Islam, Rishabh Maheshwary, Drishti Sharma, Gusti Winata, Nathan Lambert, Sebastian Ruder, Sara Hooker, Marzieh Fadaee
2024-10-24
Summary
This paper introduces M-RewardBench, a new evaluation benchmark designed to assess how well reward models (RMs) perform in multiple languages, helping improve large language models (LLMs) that use human feedback.
What's the problem?
Most reward models have been trained and tested only in English, which means we don't know how well they work in other languages. This lack of understanding can lead to poor performance when these models are used for multilingual tasks, as they might not align with human preferences across different languages.
What's the solution?
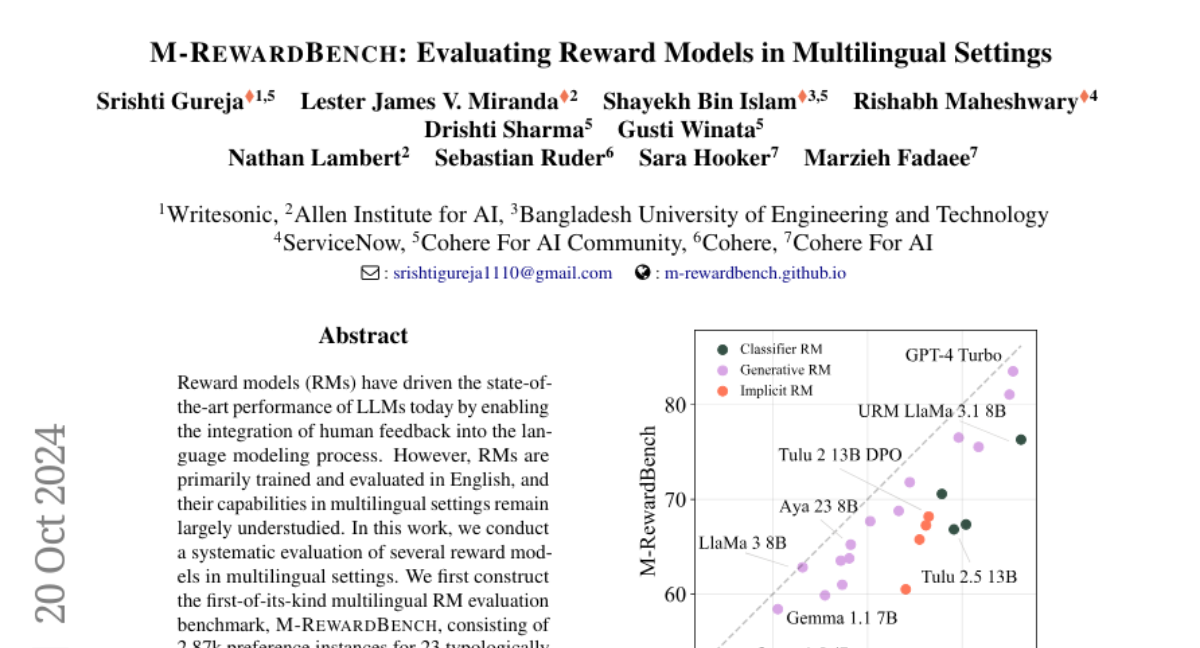
The authors created M-RewardBench, the first multilingual evaluation benchmark that includes nearly 3,000 preference examples across 23 different languages. They tested various reward models on this benchmark to see how well they perform in areas like chat, safety, reasoning, and translation. Their findings showed that there are significant differences in how well these models perform in English compared to other languages, and that the quality of translations affects their performance.
Why it matters?
This research is important because it highlights the need for better evaluation of language models in multilingual settings. By understanding how reward models function across different languages, we can improve their effectiveness and create more reliable AI systems that cater to diverse populations.
Abstract
Reward models (RMs) have driven the state-of-the-art performance of LLMs today by enabling the integration of human feedback into the language modeling process. However, RMs are primarily trained and evaluated in English, and their capabilities in multilingual settings remain largely understudied. In this work, we conduct a systematic evaluation of several reward models in multilingual settings. We first construct the first-of-its-kind multilingual RM evaluation benchmark, M-RewardBench, consisting of 2.87k preference instances for 23 typologically diverse languages, that tests the chat, safety, reasoning, and translation capabilities of RMs. We then rigorously evaluate a wide range of reward models on M-RewardBench, offering fresh insights into their performance across diverse languages. We identify a significant gap in RMs' performances between English and non-English languages and show that RM preferences can change substantially from one language to another. We also present several findings on how different multilingual aspects impact RM performance. Specifically, we show that the performance of RMs is improved with improved translation quality. Similarly, we demonstrate that the models exhibit better performance for high-resource languages. We release M-RewardBench dataset and the codebase in this study to facilitate a better understanding of RM evaluation in multilingual settings.