MathFusion: Enhancing Mathematic Problem-solving of LLM through Instruction Fusion
Qizhi Pei, Lijun Wu, Zhuoshi Pan, Yu Li, Honglin Lin, Chenlin Ming, Xin Gao, Conghui He, Rui Yan
2025-03-21
Summary
This paper is about improving how well AI can solve math problems by teaching it in a way that connects different math concepts together.
What's the problem?
AI models often struggle with math because they learn concepts in isolation, without understanding how they relate to each other.
What's the solution?
The researchers created a method called MathFusion that teaches AI by combining different math problems and showing how they're connected, like linking geometry and algebra problems.
Why it matters?
This work matters because it can make AI better at understanding and solving complex math problems, which can be useful in many fields.
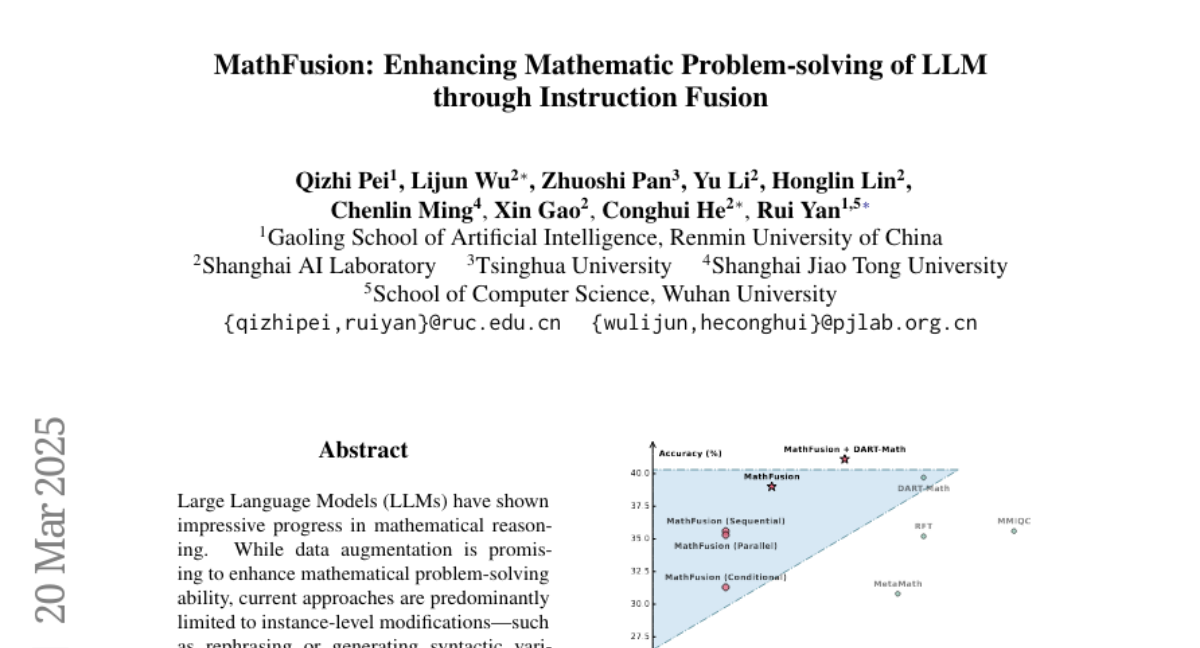
Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive progress in mathematical reasoning. While data augmentation is promising to enhance mathematical problem-solving ability, current approaches are predominantly limited to instance-level modifications-such as rephrasing or generating syntactic variations-which fail to capture and leverage the intrinsic relational structures inherent in mathematical knowledge. Inspired by human learning processes, where mathematical proficiency develops through systematic exposure to interconnected concepts, we introduce MathFusion, a novel framework that enhances mathematical reasoning through cross-problem instruction synthesis. MathFusion implements this through three fusion strategies: (1) sequential fusion, which chains related problems to model solution dependencies; (2) parallel fusion, which combines analogous problems to reinforce conceptual understanding; and (3) conditional fusion, which creates context-aware selective problems to enhance reasoning flexibility. By applying these strategies, we generate a new dataset, MathFusionQA, followed by fine-tuning models (DeepSeekMath-7B, Mistral-7B, Llama3-8B) on it. Experimental results demonstrate that MathFusion achieves substantial improvements in mathematical reasoning while maintaining high data efficiency, boosting performance by 18.0 points in accuracy across diverse benchmarks while requiring only 45K additional synthetic instructions, representing a substantial improvement over traditional single-instruction approaches. Our datasets, models, and code are publicly available at https://github.com/QizhiPei/mathfusion.