Your ViT is Secretly an Image Segmentation Model
Tommie Kerssies, Niccolò Cavagnero, Alexander Hermans, Narges Norouzi, Giuseppe Averta, Bastian Leibe, Gijs Dubbelman, Daan de Geus
2025-03-31
Summary
This paper is about how a type of AI model called a Vision Transformer (ViT), which is usually used for identifying objects in images, can also be used to figure out what each individual pixel in an image represents.
What's the problem?
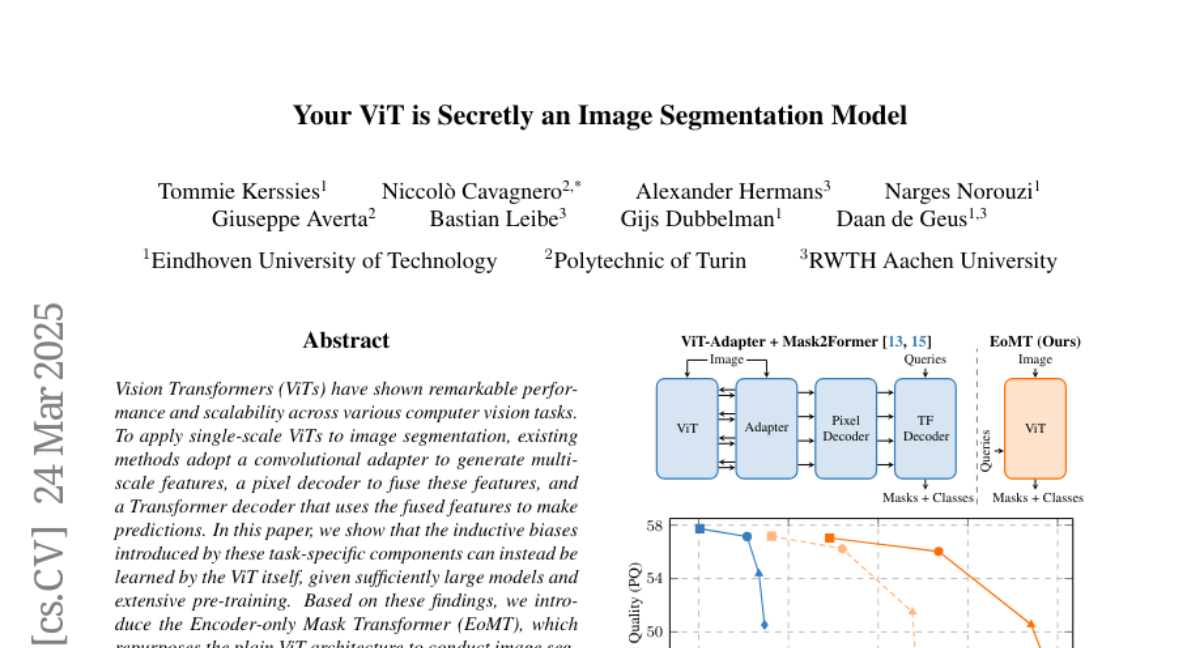
To use ViTs for image segmentation (labeling each pixel), people usually add extra components to the model, making it more complicated.
What's the solution?
The researchers found that if you make the ViT big enough and train it well, it can do image segmentation without those extra components, making it faster and simpler.
Why it matters?
This work matters because it shows that we can use simpler AI models for complex tasks, which can save time and resources.
Abstract
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable performance and scalability across various computer vision tasks. To apply single-scale ViTs to image segmentation, existing methods adopt a convolutional adapter to generate multi-scale features, a pixel decoder to fuse these features, and a Transformer decoder that uses the fused features to make predictions. In this paper, we show that the inductive biases introduced by these task-specific components can instead be learned by the ViT itself, given sufficiently large models and extensive pre-training. Based on these findings, we introduce the Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT), which repurposes the plain ViT architecture to conduct image segmentation. With large-scale models and pre-training, EoMT obtains a segmentation accuracy similar to state-of-the-art models that use task-specific components. At the same time, EoMT is significantly faster than these methods due to its architectural simplicity, e.g., up to 4x faster with ViT-L. Across a range of model sizes, EoMT demonstrates an optimal balance between segmentation accuracy and prediction speed, suggesting that compute resources are better spent on scaling the ViT itself rather than adding architectural complexity. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/.